TM 9-4940-444-14 & P
EXHAUST PIPING INSTRUCTIONS - cont
N. Hoods and Enclosures.
Whenever hoods and enclosures are constructed of sheet metal, the materials used should generally conform to the
kind of material specified for the piping. Because the hoods and enclosures will vary in size, shape and construction
due to the particular application, no specific rules can be given covering all of the elements of design, but the hoods
and enclosures shall be constructed and provided with sufficient reinforcement to make them structurally permanent
and all joints shall be tight to prevent air leakage.
O. Flexible Piping and Joints.
1. Flexible Piping:
If flexible piping connections are required because of adjustable hoods, such as on stationary pedestal grinders, or
hoods adjusted to suit operating conditions, such as surface and cutter grinders and certain swing frame grinder
applications and the like, the hoods shall be connected to the branch pipes by means of flexible piping of the same
internal diameter as the hood outlet and branch of one of the following specifications:
Rubber tubing with a smooth interior and reinforced with a spiral wire built in as an integral part of the tubing. The
wire reinforcement is necessary to prevent the walls of the tubing from collapsing under suction and to retain full
inside diameter when the tubing is bent or kinked.
Electro-galvanized steel flexible metal tubing square locked with heavy asbestos packing for the elimination of air
leakage into the exhaust system.
For handling exhaust gases under pressure as from an engine exhaust or where there is danger of leakage
outward around the flexible piping, piping shall be electro-galvanized steel.
2. Flexible Joints:
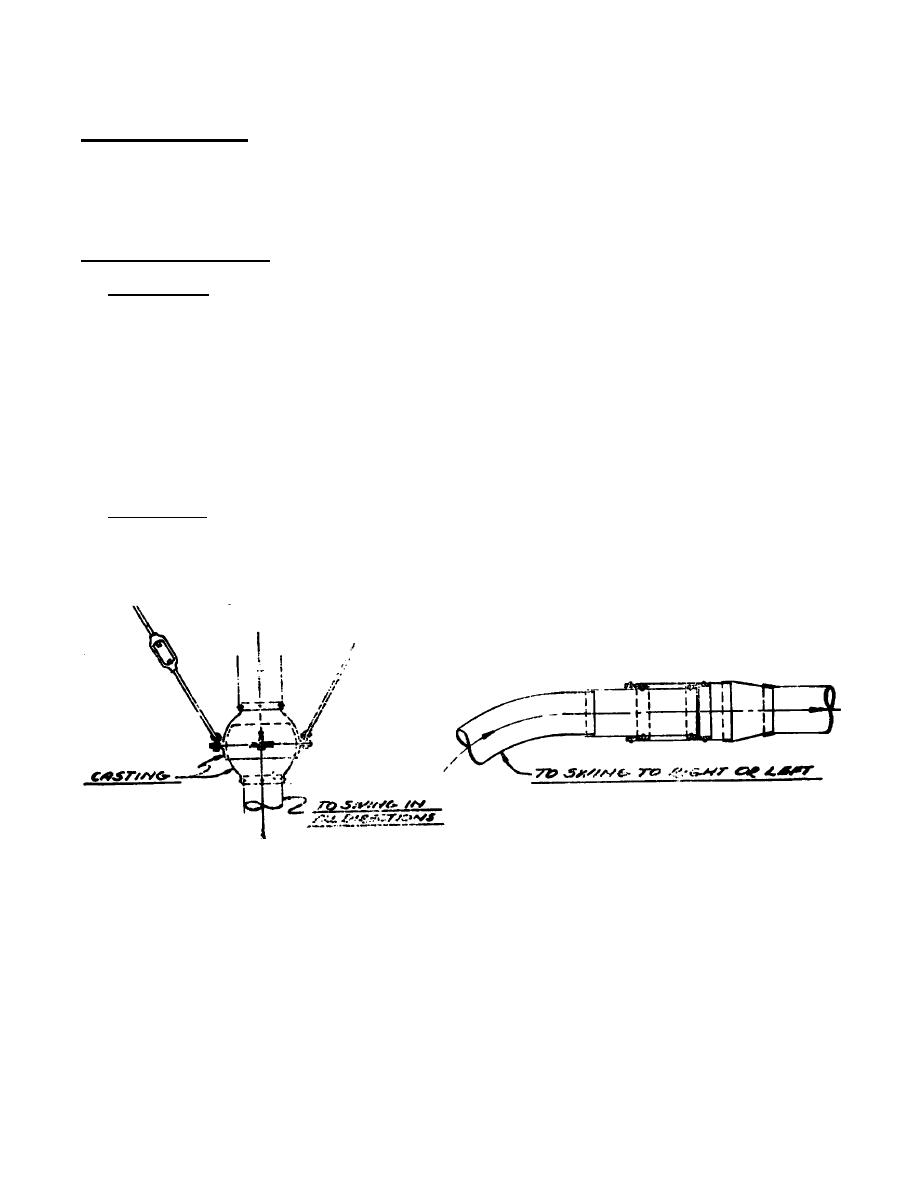
a. Swing Joints - if some flexibility is required in a pipe joint to permit the swinging of the hood about the
branch pipe, such swinging or roller Joints shall be constructed as per swinging Joint construction shown
below. Such joints shall be made as air tight as possible to eliminate excessive leakage.
82


