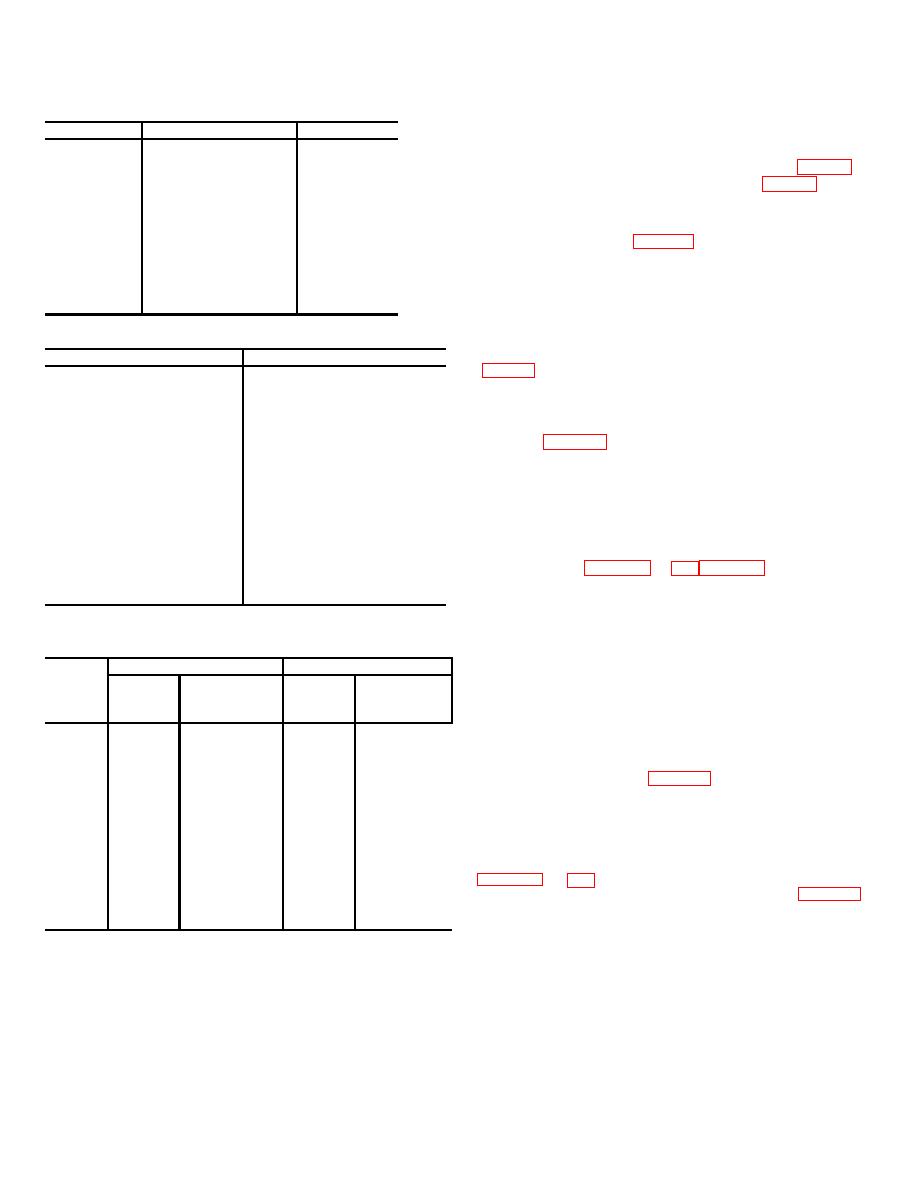
Table 2. Species of Wood Most Commonly Used
For Bracing
(4) In order to reinforce cross car bracing,
Soft woods
Medium woods
Hard woods
diagonal braces extending from the cross brace to the car
Cedar
Douglas Fir
Ash
walls are used to supplement the strength of the cross brace.
Chestnut
Hemlock
Beech
This forms what is known as a K brace as shown in figure 5.
Cottonwood
Maple
Elm
Another adaptation of the K brace is shown in figure 8. In this
Fir, Alpine
Larch
Hickory
example, a single K brace reinforces two cross braces.
Fir, Balsam
Pine
(Northern
Maple (Hard)
(5) The reinforcement of cross car bracing to car
Carolina)
floors can be provided by the use of diagonal bracing to the
car floor as shown in figure 9. The bracing must not be
Fir, White
Pine (Southern Yellow)
Oak
applied at an angle greater than 45 degrees with the car floor.
Pine, Jack
Ash
It is desirable that the cross brace be positioned at a point
Pine, White
approximately one-third down from the top of the load. Table
Spruce
6 shows the minimum length of diagonal braces in relation to
Poplar
height of cross brace above car floor.
(6) Knee braces should be used to prevent
Table 3. Soft and Medium Woods (Standard Sizes)
dislodgment or bowing of floor diagonals and should be
applied at right angles to the floor diagonals, as shown in
Medium woods (in.)
Soft woods (in.)
Size 3/8 x 1 (Lath)
Size 3/8 x 1 (Lath)
(7) Top bracing will be found desirable in many
Size x 4
Size 3/4 x 4
instances to prevent upward movement of a load. The
Size 1 x 2
Size 1/4 x 2
security of this type of bracing is dependent upon the proper
Size 1 x 3
Size 1/4 x 3
application of pocket cleats. Two methods of top bracing are
Size 1 x 4
Size 1/4 x 4
shown in figure 10. Diagonal reinforcement is used for heavy
Size 1 x 6
Size 1/4 x6
loads. However, the top ends of these diagonals should never
be placed at the intersection of the roof and side walls of the
Size 2 x 2
Size 2 x 2
car, but should be backed up with cleats and the diagonal
Size 2 x 3
Size 2 x 3
braces.
Size 2 x 4
Size 2 x 4
(8) Bracing used to prevent top-heavy articles
Size 2 x 6
Size 2 x 6
from falling or tipping over in transit should be placed at a
Size 3 x 4
Size 4 x 4
point approximately opposite the upper third of the article.
Size 4 x 4
Size 4 x 5
This type of bracing' is commonly referred to as collar bracing
Size 4 x 6
Size 5 x 6
and is shown in figures 11 and 12. Figure 11 shows two types
Size 6 x 6
Size 6 x 7
of machines, A and B. Type A is of solid cast iron base
construction and should be blocked against the skid members
Size 6 x 8
Size 7 x 8
as shown.
Type B, which is a leg-type construction, must not be blocked
Table 4. Cement-Coated Nails and Round Wire
crosswise against the ends of the skid members.
Spikes
(9) When commodities in containers are loaded in
Cement-coated nails
Round wire spikes
more than one layer, filler boards should be used to provide
an even base for the containers in the upper layers. Fillers
Length
Gauge No.
Length
Gauge No.
must be of sound material at least 1-inch thick to carry the
(in.)
(in.)
or size (in.)
weight of the load, and must be placed lengthwise in the car.
Size
To hold these fillers securely in place, a crosswise board of 2-
10d*
2 7/8
11
3
6
inch x 4-inch material should be securely nailed to each
12d
3 1/8
10
3 1/4
6
lengthwise filler board. When the load is rigidly braced, this
16d
3 1/4
9
3 1/2
5
unit can then be held in position by means of cleats affixed to
the cars walls, as shown in figure 13.
20d
3 3/4
7
4
4
(10) Location of the inside blocking should be
30d
4 1/4
6
4 1/2
3
marked on the outside of the container in order that the car
40d
4 3/4
5
5
2
loader can determine where to apply blocking.
50d
5 1/4
4
5 1/2
1
(11) Incomplete layers in shipments should be
60d
5 3/4
3
6
1
avoided whenever possible.
However, when incomplete
7 in.
7
5/16 in.
layers have to be loaded, crosswise bracing as shown in
8 in.
8
3/8 in.
9 in.
9
3/8 in.
secured to car walls with pocket cleats, as shown in figure 15.
10 in.
10
3/8 in.
12 in.
12
3/8 in.
*d-Penny
7


