Table 5. Sizes of Nails, Spikes, and Bolts for Various Thicknesses of Material
Thickness of material
Thickness of material (rough lumber) holding point of nail(in.)
(rough lumber) holding
head of nail or spike
(in.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
6d*
10d
16d
16d
16d
16d
8d**
12d**
2
16d
20d
40d
40d
40d
30d
50d
60d
60d
3
30d
40d
60d
Bolt
60d
7-in.
7-in.
8-in.
Spike
Spike
Spike
4
Bolt
Bolt
Bolt or
Bolt or
Bolt or
7-in.
7-in.
7-in.
Spike
Spike
Spike
5
Bolt
Bolt
Bolt
Bolt or
Bolt or
9-in.
10-in.
Spike
Spike
6
Bolt
Bolt
Bolt
Bolt
Bolt or
10-in.
Spike
*d-Penny
"*Nails clinched
Table 6. Length of Diagonals to Car Floor
Height of application of diag-
Minimum length of diagonal
onal brace to cross brace or load
brace required
load above car floor
(ft)
(in.)
(ft)
(in.)
1
0
1
6
1
6
2
3
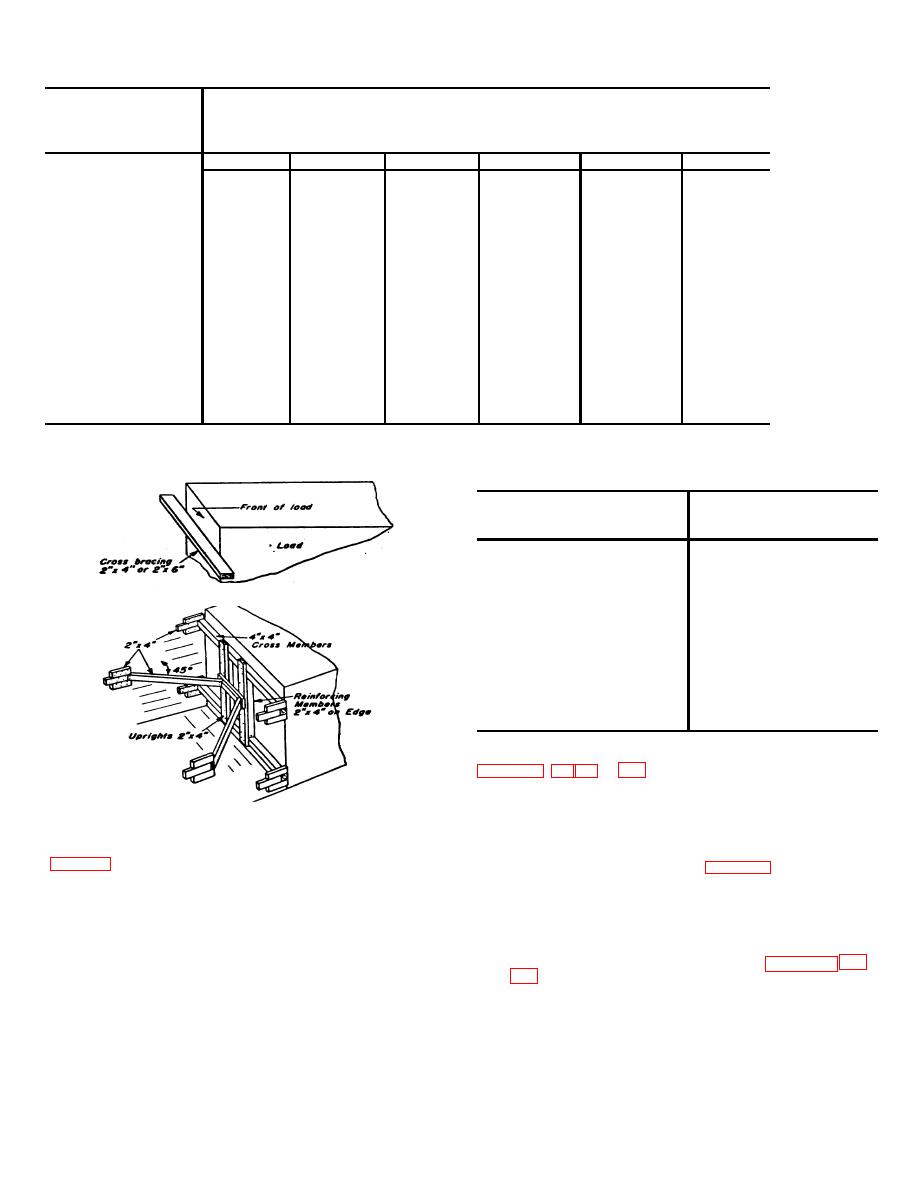
Figure 7. Cross car bracing.
2
0
3
0
2
6
3
6
3
0
4
3
3
6
5
0
4
0
5
9
4
6
6
6
5
0
7
3
5
6
7
9
6
0
8
6
ment of lading can be used. Some examples are shown in
d. Gates.
(1) Gates are structures used to fill the lengthwise
Figure 8. Single K brace reinforcing cross braces.
space in a car not occupied by the lading, or to segregate the
lading. Gates are designated according to types, such as end
gates, divisional or intermediate gates, and center gates.
Cross bracing can also be secured in position, as shown in
(2) End gates, shown in figure 21, should be used
when commodities in fiberboard containers or light crates are
stowed in cars equipped with unlined corrugated steel ends so
(12) When the lading does not completely fill the
as to provide a smooth surface for the lading. End gates can
car crosswise, various forms of construction for side or center
also be used at one or both ends of the car to take up
bracing to prevent move-
lengthwise space in lieu of a center gate, if the shipper desires
to use a through load.
(3) Divisional gates, as shown in figures 22, 23,
and 24, are used to secure separate units in the load or to
segregate different types of containers or commodities.
These gates should be held in position by means of blocking
secured to
8


